Retinopathy is a condition that affects the retina, the vital tissue lining the back of our eyes. It is most commonly associated with diabetes, but can also be caused by other eye diseases and high blood pressure. As ophthalmology continues to advance, it becomes increasingly important to shed light on retinopathy, its detection, and the potential consequences if left untreated.
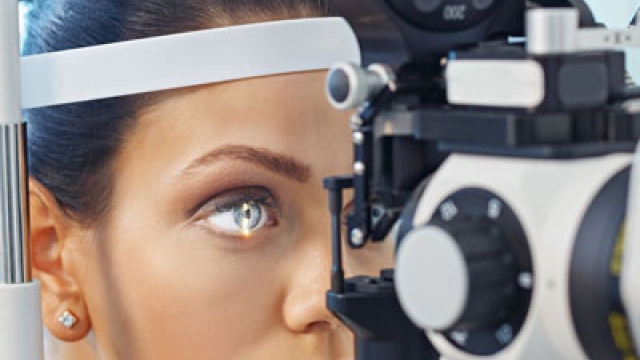
One key aspect in the battle against retinopathy is the early detection and intervention through diabetic eye screening. This specialized screening process plays a crucial role in identifying retinal abnormalities at an early stage, even before symptoms become apparent. By regularly undergoing these screenings, individuals with diabetes can ensure that any signs of retinopathy are detected promptly, allowing for timely medical intervention to prevent further deterioration of their vision.
However, it is essential to recognize that retinopathy is not limited to diabetic individuals alone. Anyone can be susceptible to this condition, particularly those with a family history of eye disease or high blood pressure. Glaucoma, another prevalent eye condition, is also often linked to retinopathy. Therefore, understanding retinopathy and its potential presence in our lives becomes significant for everyone, not just those with diabetes.
Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the realm of retinopathy, exploring the risk factors, early signs to watch out for, available treatment options, and the importance of regular eye check-ups. Together, we will strive to increase awareness and empower ourselves to take charge of our eye health, ultimately seeing through the shadows of retinopathy.
What is Retinopathy?
Retinopathy is a condition that affects the retina, a vital part of our eyes responsible for capturing images and sending signals to the brain for processing. It is most commonly associated with diabetes but can also be caused by other factors such as high blood pressure, glaucoma, and certain medications.
In the case of diabetic retinopathy, high levels of blood sugar can gradually damage the small blood vessels within the retina, leading to a variety of vision problems. Initially, the early stages of retinopathy may not exhibit any noticeable symptoms, hence the importance of regular ophthalmology check-ups and diabetic eye screenings.
As the condition progresses, symptoms may begin to manifest, including blurred or distorted vision, dark spots or floaters, and even complete vision loss in severe cases. It is crucial to detect and diagnose retinopathy early to prevent further damage and preserve vision. Regular screenings and appropriate management can play a significant role in preventing complications and maintaining eye health.
Detecting and Diagnosing Retinopathy
The early detection and diagnosis of retinopathy are crucial in preventing vision loss and managing the condition effectively. Ophthalmologists play a vital role in this process, as they specialize in diagnosing and treating diseases of the eye, including retinopathy.
One of the key methods used in the detection of retinopathy is diabetic eye screening. This screening involves the use of specialized instruments and techniques to examine the retina for any signs of damage or abnormalities. By conducting regular screenings, ophthalmologists can identify retinopathy at its early stages, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment.
In addition to diabetic eye screening, ophthalmologists also rely on various diagnostic tests to accurately assess the severity of retinopathy. These tests may include visual acuity tests, which measure the sharpness of the patient’s vision, and intraocular pressure tests, which help detect glaucoma, a condition often associated with retinopathy. Furthermore, advanced imaging technologies such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography enable ophthalmologists to visualize and analyze the structures within the retina, facilitating the diagnosis and monitoring of retinopathy.
In conclusion, timely detection and diagnosis are essential in managing retinopathy effectively. Ophthalmologists employ diabetic eye screening, along with a combination of diagnostic tests, to accurately assess the condition and formulate appropriate treatment plans. By utilizing these tools and techniques, ophthalmologists can help patients navigate the challenges posed by retinopathy and preserve their visual health.

Managing and Treating Retinopathy
Visit Website
In the battle against retinopathy, effective management and treatment play a crucial role in preserving vision and preventing further damage. Ophthalmology professionals employ a range of strategies tailored to each patient’s condition, helping them navigate the complexities of this eye disease.
The first step in managing retinopathy is early detection through regular diabetic eye screening. These screenings allow ophthalmologists to identify any signs of retinopathy at an early stage when treatment options are more effective. By closely monitoring the progression of the disease, ophthalmologists can intervene promptly and implement personalized treatment plans.
Once diagnosed, treatment focuses on minimizing the impact of retinopathy on vision. Laser therapy, also known as photocoagulation, is a commonly used technique in which a laser beam is used to seal off leaking blood vessels and reduce swelling. This procedure helps prevent vision loss and stabilize the condition. In some cases, medication can be prescribed to control the underlying factors contributing to retinopathy, such as high blood pressure or blood sugar levels.
Another critical aspect of managing retinopathy is addressing the risk of developing glaucoma, a co-existing condition commonly associated with this eye disease. Ophthalmologists may recommend regular monitoring of intraocular pressure and suggest treatments to control glaucoma if necessary. By addressing both retinopathy and glaucoma together, healthcare professionals can provide a comprehensive approach to preserving vision and managing these conditions effectively.
In conclusion, managing and treating retinopathy hinges on early detection, personalized treatment plans, and addressing related conditions like glaucoma. These strategies work hand in hand to protect vision and enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by retinopathy. Through advancements in ophthalmology and diabetic eye screening programs, we can continue to make significant strides in preventing and managing this sight-threatening disease.